Conditions – Breast Disease
Benign breast disease
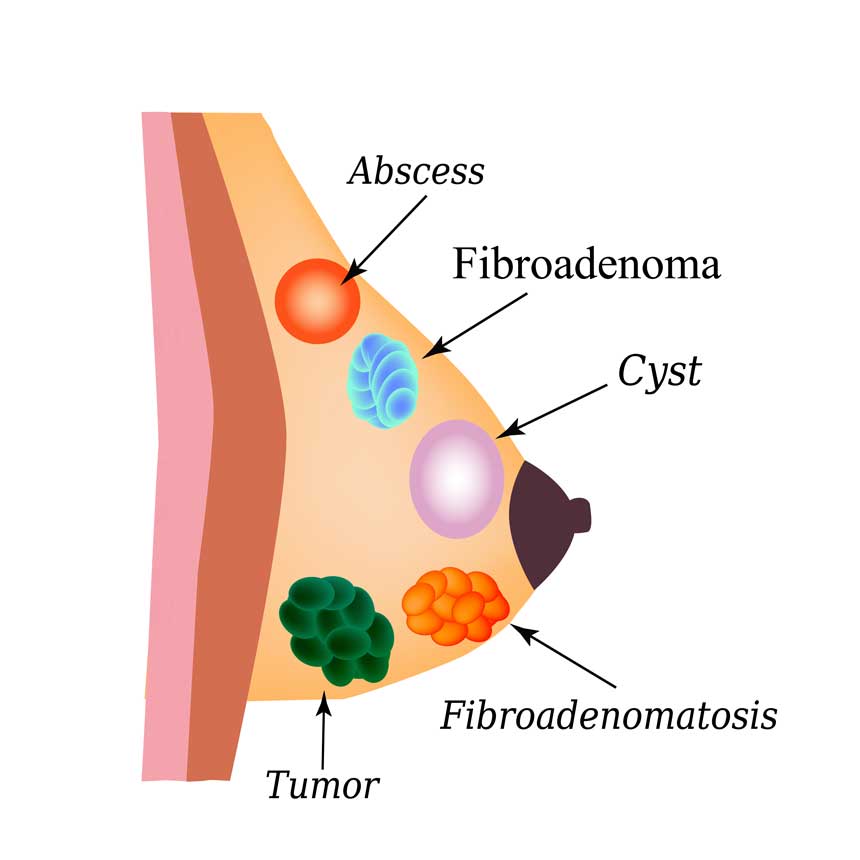
Fibroadenoma
These benign lumps account for up to 3 in 5 lumps found in women age 18 to 25 and 1 in 7 breast lumps found in general. Up to the age of 25 the breast is considered to be still developing and during development these benign lumps form. These are normally smooth and can be moved around in the breast (like a breast mouse) and normally have no other symptoms.
A careful history and examination will be performed to help establish the diagnosis. An Ultrasound scan will be required to confirm the diagnosis. Usually in lumps greater than 3cm a biopsy will be performed to ensure that the lump is benign.
With time one in three fibroadenomas will reduce in size, one in ten will grow bigger, while the rest will remain the same. During pregnancy these fibroadenomas do tend to grow in size. Usually small fibroadenomas less than 3 cm just need monitoring without the need of any biopsy or surgery. In bigger fibroadenomas, in those that continue to grow, if you are older than 35 years of age or if you wish to have the lump removed a breast lumpectomy can be performed.
Breast cyst
These are fluid filled swellings in the breast that tend to occur around the time of the menopause. They account for one in seven breast lumps found. These are felt as smooth soft swelling in the breast and can sometimes develop fast and be painful. A mammogram and/or an ultrasound of the breast are usually required to rule out any other underlying lesion. Drainage of the fluid from the cyst under ultrasound guidance is used to help rule out any malignancy and also as treatment. Breast lumpectomy can be performed if the cyst returns back very fast or many times or if there is an area of suspicion.
Breast papilloma
This is a wart like benign lump that can develop in the breast ducts usually around the nipple area. They are more common in women over the age of 40. They can be felt as small lumps or cause a clear or blood-stained discharge from the nipple. These lumps do not have a risk of turning into a cancer unless any abnormal cells are found in them when biopsied. Breast papillomas are diagnosed through a combination of examination, x-ray or ultrasound and biopsies. If you have any abnormal cells then a breast lumpectomy will be required while if there is persistent nipple discharge the breast ducts under the nipple can be removed (Hadfield’s procedure).
Choose Category
– Breast cancer
– Benign breast disease Fibroadenoma, Papilloma, Breast cyst
– Breast abscess
Need to contact us or book an appointment?
Disclaimer
The information relating to general and colorectal disorders and their treatments given on this website is not complete and is not intended as a substitute for a consultation with your doctor. Always seek medical advice from your doctor before making a decision about any of the conditions and/or treatments mentioned on this website.
© Dr Georgios Markides
Contact Information
You can always contact our Clinic for booking appointments and other useful information:
Dr. Georgios Markides,
Consultant General & Colorectal Surgeon
APEX Building, 47 Andreas Avraamides Str., 2024 Strovolos, Nicosia, Cyprus
+357-22-282008
