Conditions – Colon and Rectum
Diverticulosis
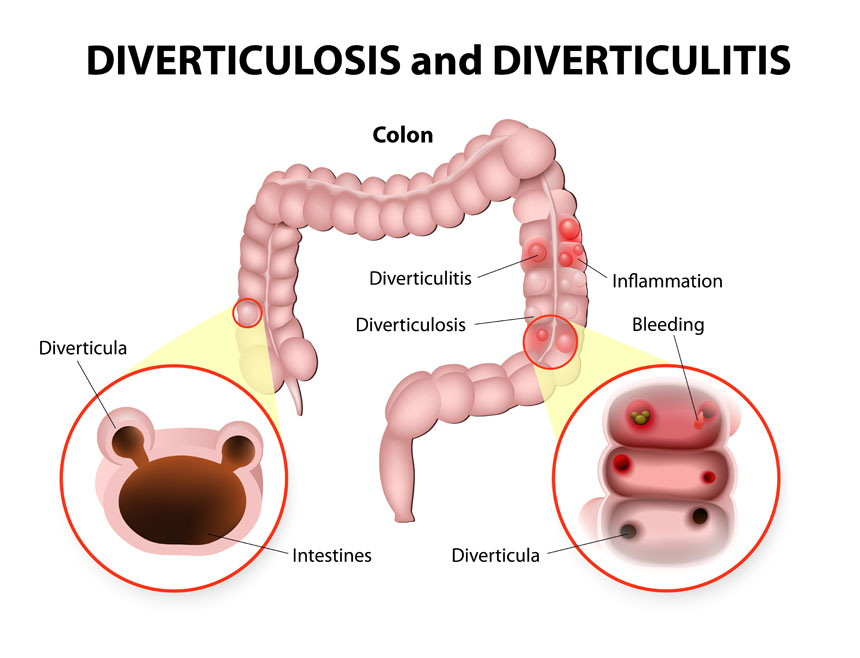
Diverticulosis is a very common condition of the large bowel especially in the West. It can affect one in ten people over the age of 40 and up to half of people over the age of 65. The cause is thought to be diet related to the lack of fibre in the diet leading to harder motions and higher pressures within the bowel lumen. This leads to the formation of diverticulae which are small abnormal pouches that form in the lining of the bowel. Obesity and lack of exercise are additional risk factors.
Symptoms
Many people with diverticular disease will have no symptoms. Some people though may develop symptoms of:
- a change in their bowel habit into either looser or more solid stools,
- the diverticulae can bleed,
- can be the cause of abdominal pain or
- can form narrowing of the bowel.
They can sometimes also become infected or inflamed (diverticulitis) with fever and abdominal pain and may lead to perforation of the bowel forming a local abscess or release of bowel content inside the abdomen requiring emergency surgery. More rarely an abnormal connection (fistula) can form between the bowel and the urinary bladder, vagina or skin.
Investigations
Once a history of your symptoms is taken and you are examined, a number of investigations will be required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. This includes blood tests, a urine test, a pregnancy test for women and a stool test. The definitive diagnosis of diverticular disease is usually made through the use of a colonoscopy. If diverticulitis is suspected then a CT scan will be required with a colonoscopy taking place a few weeks later once the attack has settled to confirm the diagnosis and exclude any sinister cause.
Treatment
The treatment of diverticular disease depends on the symptoms it is causing. Exercise with a high fibre diet and increased fluid intake is beneficial in avoiding worsening of the condition. In cases were the symptoms are affecting your quality of life then surgery in the form of bowel resection may be required to remove the diseased part of the bowel. The surgery can be performed laparoscopically (laparoscopic colectomy) in most cases.
In cases of simple diverticulitis the use of painkillers and antibiotics may be enough to settle down the condition. In more serious cases or in cases of bowel perforation the insertion of a drain or emergency surgery may be required. This may sometimes involve a washout of any pus inside the abdomen and insertion of drains (diagnostic laparoscopy and washout) or removal of the diseased bowel with the potential formation of a stoma (Hartmann’s procedure). These procedures may be performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic (keyhole) techniques or through open surgery.
Choose Category
– Colorectal cancer
– Colorectal polyps
– Diverticulosis
– Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s
– Stoma
– Abdominal pain
– Constipation
Need to contact us or book an appointment?
Disclaimer
The information relating to general and colorectal disorders and their treatments given on this website is not complete and is not intended as a substitute for a consultation with your doctor. Always seek medical advice from your doctor before making a decision about any of the conditions and/or treatments mentioned on this website.
© Dr Georgios Markides
Contact Information
You can always contact our Clinic for booking appointments and other useful information:
Dr. Georgios Markides,
Consultant General & Colorectal Surgeon
APEX Building, 47 Andreas Avraamides Str., 2024 Strovolos, Nicosia, Cyprus
+357-22-282008
